Have you ever wondered what role sleep plays in weight loss? I mean, we all know that eating healthy and exercising regularly are important for shedding those extra pounds. But what about sleep? Is it just something we do in between our healthy meals and gym sessions? Well, you might be surprised to learn that getting enough quality sleep actually plays a significant role in weight loss. In fact, it can have a big impact on your overall health and well-being.
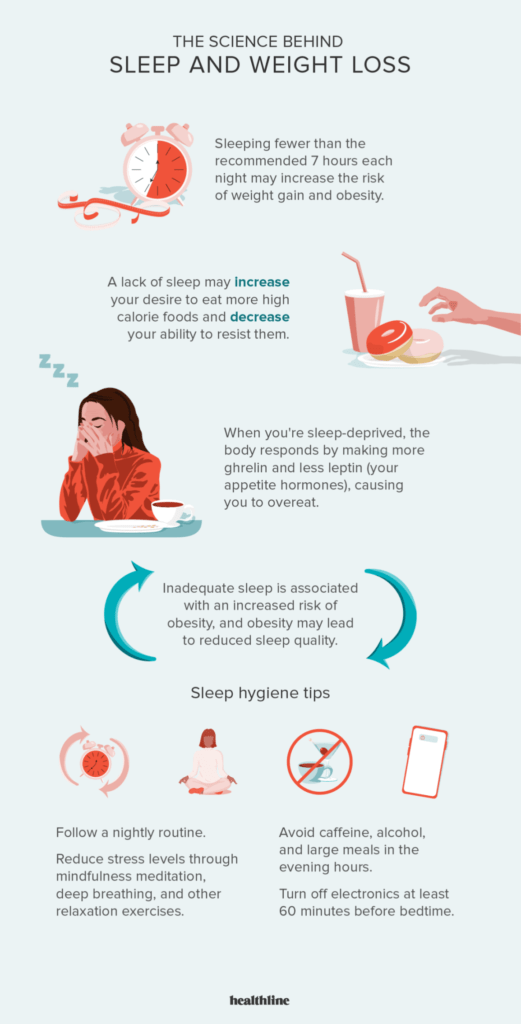
So, how exactly does sleep affect your weight? For starters, when you don’t get enough sleep, it can mess with your hormones. Lack of sleep can increase the levels of ghrelin, a hormone that tells your body it’s time to eat, while decreasing the levels of leptin, a hormone that tells your body you’re full. The result? You end up feeling hungrier and less satisfied after meals, which can lead to overeating and weight gain. Not to mention, when you’re tired, you’re more likely to reach for unhealthy, sugary snacks for a quick energy boost.
But that’s not all. Lack of sleep can also affect your body’s ability to burn calories. When you don’t get enough sleep, your metabolism slows down, making it harder for your body to burn off those extra calories. Additionally, sleep deprivation can lead to increased insulin resistance, which can make it harder for your body to regulate blood sugar levels and can eventually lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. Plus, being tired all the time can make it harder to find the motivation to exercise and stick to a healthy eating plan.
So, if you’re trying to lose weight, getting enough quality sleep should be a top priority. In the next article, we’ll dive deeper into the topic and explore some practical tips for improving your sleep and maximizing your weight loss efforts. Stay tuned! Sleep plays an important role in weight loss. Many people may not realize the impact that sleep can have on their weight and overall health. In this article, we will explore the connection between sleep and weight loss, and discuss how sleep deprivation can lead to increased appetite, hormonal imbalances, and a slower metabolism. We will also provide strategies for improving sleep and its impact on weight management. So, let’s dive in and discover the crucial role that sleep plays in your weight loss journey.
Sleep Deprivation and Increased Appetite
Sleep Deprivation and Ghrelin Levels
When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more of a hormone called ghrelin, which is responsible for stimulating hunger. Studies have shown that sleep deprivation can significantly increase ghrelin levels, leading to an increased appetite and food cravings throughout the day. This makes it harder to stick to a healthy eating plan and can contribute to weight gain.
Reduced Leptin Levels and Sleep Loss
On the other hand, sleep deprivation can also suppress the production of another hormone called leptin. Leptin is responsible for signaling to your brain that you are full and satisfied after a meal. When leptin levels are low, you may experience an insatiable hunger and find it difficult to feel satisfied even after eating. This imbalance in hunger and fullness cues can lead to overeating and weight gain.
The Influence of Sleep on Hunger Hormones
Not only does sleep deprivation affect ghrelin and leptin levels, but it also disrupts the balance between these two hormones. This can create a vicious cycle of increased appetite and reduced satiety, making it challenging to control your food intake. When you are sleep-deprived, your body’s hunger and fullness signals become out of sync, leading to overeating and a higher caloric intake.
The Connection between Sleep and Hormones
Cortisol, Stress, and Sleep
Lack of sleep can cause an increase in stress levels, which leads to the release of cortisol, known as the stress hormone. Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt your sleep patterns, causing difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. Chronic stress and disrupted sleep can contribute to weight gain, as cortisol can promote the accumulation of abdominal fat.
Insulin Resistance and Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation has also been linked to insulin resistance, a condition where your body becomes less responsive to the hormone insulin. Insulin is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, and when the body becomes resistant to its effects, it can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Getting enough sleep is crucial in maintaining healthy insulin levels and metabolic function.
The Impact of Sleep on Growth Hormone
During deep sleep, your body naturally releases growth hormone, which plays a significant role in tissue repair, muscle growth, and fat metabolism. This hormone is essential for maintaining a healthy body composition and boosting your metabolism. When you lack sufficient sleep, the production of growth hormone is diminished, affecting your body’s ability to burn fat efficiently and build lean muscle mass.

The Effect of Sleep on Metabolism
Basal Metabolic Rate and Sleep Duration
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) refers to the number of calories your body needs at rest to maintain basic bodily functions. Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy BMR. Sleep deprivation can lower your BMR, making it harder for your body to burn calories efficiently. This can lead to weight gain or hinder weight loss efforts.
Thermogenesis and Sleep Quality
Thermogenesis refers to the body’s ability to generate heat and burn calories. Sleep deprivation can decrease thermogenesis, making it more challenging for your body to effectively burn calories throughout the day. Additionally, poor sleep quality can disrupt thermoregulation, impairing your body’s natural ability to regulate temperature and burn calories.
Brown Fat Activation during Sleep
Recent studies have highlighted the role of brown fat, a type of fat that has the ability to burn calories and generate heat. Brown fat activation is highest during sleep, especially in colder temperatures. Adequate sleep and maintaining a cool sleep environment can help activate brown fat, increasing calorie expenditure and potentially aiding in weight loss efforts.
Sleep Quality and Food Choices
The Relationship between Sleep and Cravings
Sleep deprivation can lead to increased cravings, especially for high-calorie, sugary, and fatty foods. This is because sleep loss disrupts the balance of hunger and fullness hormones, leading to a higher reward response to unhealthy foods. Lack of sleep can also impair decision-making and self-control, making it harder to resist unhealthy food choices.
Emotional Eating and Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, can contribute to emotional eating. When you are sleep-deprived, you are more likely to feel irritable, stressed, and emotionally imbalanced, which can lead to seeking comfort in food. Addressing and improving sleep quality can help reduce emotional eating episodes and support healthier food choices.
The Influence of Sleep on Food Reward
When you are sleep-deprived, your brain’s pleasure centers become more active in response to food, especially highly palatable and rewarding foods. This increases the desire for indulgent foods, making it harder to resist unhealthy temptations. Getting enough sleep helps regulate the brain’s reward system, making it easier to choose more nourishing and weight-loss-friendly foods.

Sleep Patterns and Weight Management
Sleep Duration and Body Mass Index (BMI)
Numerous studies have shown a significant association between shorter sleep duration and higher body mass index (BMI). People who consistently get less sleep tend to have a higher BMI and a higher risk of obesity. Prioritizing adequate sleep duration is therefore crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing weight gain.
Sleep Efficiency and Weight Loss
Sleep efficiency refers to the amount of time spent asleep compared to the total time spent in bed. Poor sleep efficiency, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or frequent awakenings, can impair weight loss efforts. Research suggests that individuals with higher sleep efficiency have a higher success rate in achieving and maintaining weight loss goals.
The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Weight
Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and insomnia, can have a significant impact on weight. Sleep apnea, characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, has been linked to weight gain and obesity. Insomnia, on the other hand, can disrupt sleep patterns and alter hunger and satiety hormones, leading to weight gain. Treating underlying sleep disorders can help improve sleep quality and support weight loss.
Strategies for Improving Sleep
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
One of the key strategies for improving sleep is to establish a consistent sleep schedule. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed. Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep each night, prioritizing consistent sleep timing.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Creating a sleep-friendly environment can significantly impact the quality of your sleep. Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and at a moderate temperature. Remove electronic devices, such as smartphones and tablets, from your bedroom to reduce exposure to blue light, which can disrupt your sleep cycle. Investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows can also contribute to better sleep quality.
Revising Daily Habits for Better Sleep
Certain daily habits can interfere with sleep quality. Avoid consuming caffeine or alcohol in the evening, as they can disrupt sleep patterns. Regular exercise during the day can help promote better sleep, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime. Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath, can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.

The Role of Exercise in Sleep Quality and Weight Loss
Physical Activity and Sleep Duration
Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to improve sleep quality and duration. Exercise can help reduce the symptoms of insomnia and promote better overall sleep. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week for optimal sleep benefits.
The Influence of Exercise on Sleep Quality
Exercise can also positively impact sleep quality. Studies have demonstrated that exercise can improve sleep efficiency and decrease the frequency of nighttime awakenings. Regular physical activity helps regulate circadian rhythms, the internal clock that controls sleep and wakefulness, leading to more restorative sleep.
Exercise as a Complementary Approach to Weight Loss
Pairing regular exercise with a healthy diet is a powerful strategy for weight loss. Exercise not only helps increase calorie expenditure and support the development of lean muscle mass but also improves sleep quality. Restorative sleep is essential for weight loss and overall health, making exercise a valuable complement to your weight loss journey.
The Importance of Sleep Hygiene
Tips for Creating a Bedtime Routine
Establishing a bedtime routine can help signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Try incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, gentle stretching, or reading a book. Avoid engaging in stimulating activities or using electronic devices before bed, as these can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
Reducing Exposure to Blue Light
Blue light emitted by electronic devices can disrupt your natural sleep-wake cycle. To reduce exposure, avoid using electronic devices, such as smartphones and tablets, at least one hour before bed. Consider using blue light-blocking glasses or enabling the blue light filter on your devices to minimize the impact of blue light on your sleep quality.
Avoiding Stimulants and Alcohol before Bed
Consuming stimulants, such as caffeine or nicotine, close to bedtime can interfere with falling asleep. It’s important to avoid consuming these substances in the evening or at night. Additionally, while alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy, it can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to poor-quality sleep. It’s best to avoid alcohol close to bedtime.

Conclusion
Recognizing the significance of sleep for weight loss is crucial for achieving optimal results. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased appetite, hormonal imbalances, and a slower metabolism, making weight loss more challenging. By implementing healthy sleep patterns, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and revising daily habits for better sleep, you can support your weight loss goals. Additionally, incorporating regular exercise, improving sleep hygiene, and prioritizing restorative sleep can further enhance your weight loss journey. So, make sleep a priority and reap the benefits of a well-rested body and mind on your path to weight loss success. Sweet dreams!
